Der Gebrauch von RO-Membranen ist seit Einführung im industriellen Maßstab, Mitte 1960, rasch angestiegen. Durch die Entwicklung und Markteinführung von Thin-Film-Composite im Jahre 1977 wurde die Umkehrosmose-Technologie zukunftsweisend weiterentwickelt. Heute wird eine Vielzahl von Thin-Film-Composite Membranen (Polyamid) vermarktet.
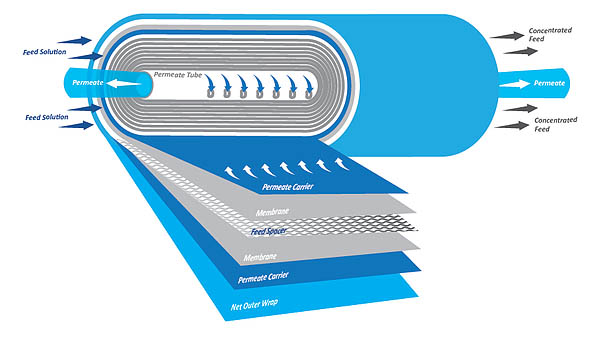
Dabei gibt es eine Reihe verschiedenster Konfigurationen; vom Platten-Rahmen-System über Rohr-Systeme bis hin zum gebräuchlichsten System, dem Wickelmodul, die auch anwendungsspezifische Bedeutung haben.
Eine Vielzahl von Anwendungen haben sich entwickelt und „traditionelle“ Verfahren abgelöst. Die weitaus häufigste Anwendung ist unter dem Oberbegriff Wasseraufbereitung zu finden. Dazu gehören Verfahren wie Enthärtung und Entsalzung von Grund-, Brunnen-, Oberflächen- und Kesselspeisewasser. Auch die Entfernung von TOC, Pestiziden, Herbiziden und anderen Umweltgiften aus Trinkwasser wird heute von RO-Membranen geleistet.
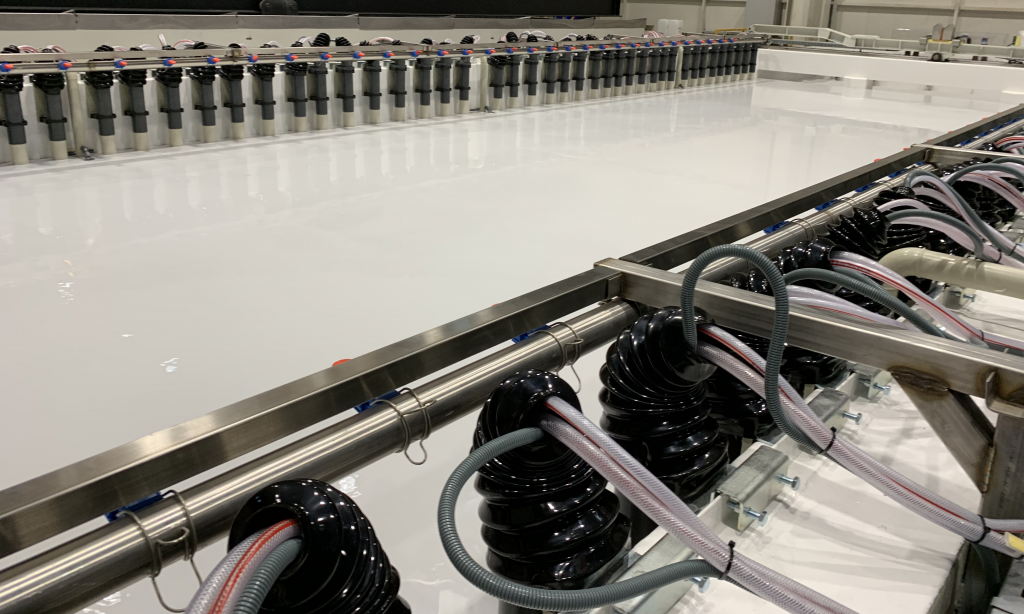
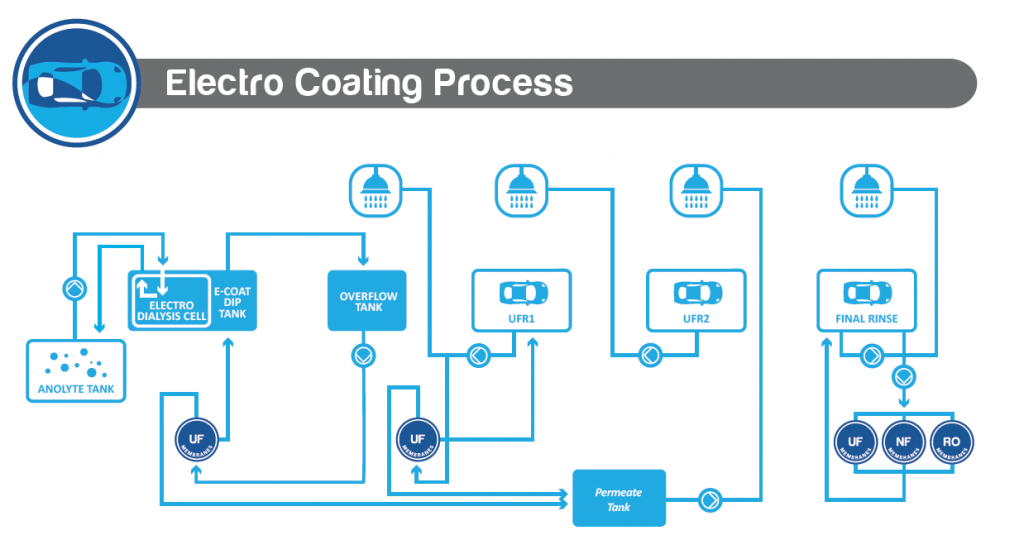
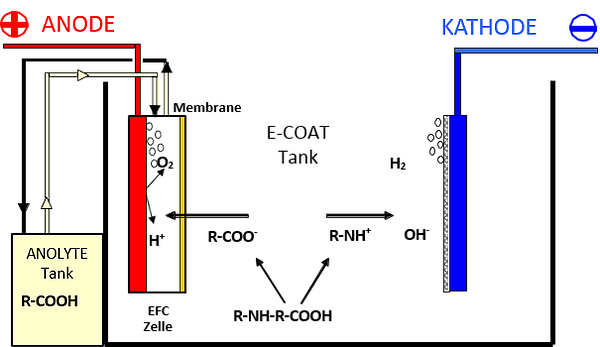
Daneben hat sich auch in anderen Industriebereichen die Umkehrosmose als eine Standardtechnologie etabliert. Bei der Prozeßstromkonzentierung in der Automobilindustrie oder in der Abwasseraufbereitung mit Kreislaufführung hat sich dieses Verfahren bereits bestens bewährt.
Durch eine veränderte Betrachtung dieser Technologie weg von der technischen Sicht “was ist möglich”, hin zu der kaufmännischen Sicht “was kostet sie”, sind neue Anforderungen an die Membranentwicklung entstanden.
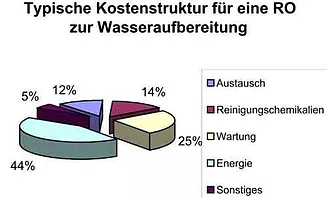
Die Wirtschaftlichkeit einer LG Chem Membrane (und damit häufig auch einer neuen Anwendung ) orientiert sich an folgenden Kriterien:
- Energieaufwand
- Arbeits- / Wartungs- / Betreuungsaufwand
- Austauschkosten der Membran
- Chemikalienaufwand bei Reinigung und Produktion
- Investitionskosten
Fouling / Scaling („Low-Fouling“-Membran”)
Durch die Auswahl von Membranmaterialien und durch entsprechende Fertigungsschritte bei der Membranherstellung ist es möglich, optimierte Membranen für verschiedenste Prozesse bereitzustellen, um prozessbedingtes Fouling gering zu halten. Unterstützt wird dies auch durch die Verfahrenstechnik wie z.B. ein höherer Cross Flow. Durch den gezielten Einsatz von Antiscaling-Mitteln in den Zulauf einer RO-Anlage oder in Kombination mit Enthärtungsverfahren, kann ein Scaling kontrolliert werden.
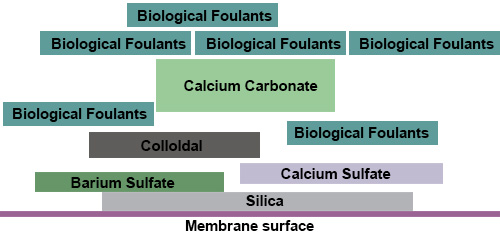
Weitere Punkte sind die Lebens- / Standzeitverbesserung und der damit in Zusammenhang stehende benötigte Chemikalieneinsatz bei der Reinigung von Membranen. Hier hat die chemische Industrie entsprechende Chemikalien entwickelt, die die Membran weniger chemisch angreifen, aber erheblich besser reinigen. Durch den Einsatz dieser Stoffe werden auch die Arbeits- und Wartungskosten des Bedienungspersonals erheblich gesenkt. Durch chemische Modifikation werden ausgesprochene „Anti-Fouling“- Membranen vom Typ AFR produziert. Einige Hersteller weisen dieses Verhalten marketingträchtig als besondere Eigenschaft aus. LG AFR-Elemente weisen diese günstige Produkteigenschaft bereits seit ihrer Markteinführung auf und stehen als HR.